Accelerating Optimization: How SimpleRose and NVIDIA cuOpt Solve Linear and Mixed-Integer Linear Programming Problems Faster
Published on March 18, 2025
March 18, 2025
Linear programming (LP) and mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) are at the core of solving operations challenges, ranging from supply chain efficiency to workforce scheduling. These problems are notoriously complex and computationally demanding.
To tackle these problems, SimpleRose and NVIDIA have joined forces to deliver cutting-edge optimization solutions that significantly reduce solve times while maintaining mathematical accuracy.
SimpleRose integrates NVIDIA cuOpt with its Rapidly Optimizing Solver Engine (Rose) to accelerate the discovery of optimal solutions for large-scale LP and MILP problems, addressing the world’s most important and complex optimization problems by uniquely leveraging NVIDIA accelerated computing.
Breaking Down Complex Optimization Challenges
Mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) is the cornerstone of decision optimization, enabling businesses to solve complex, large-scale problems across various industries. However, as problem size increases, computational demands grow exponentially, making efficient solutions critical. MILP plays a key role in:
- Supply Chain Optimization: Balancing transportation costs with delivery efficiency.
- Workforce Scheduling: Allocating resources effectively to maximize productivity and minimize downtime.
- Facility Layout Design: Addressing quadratic assignment problems (QAP) to optimize network and spatial efficiency.
- Production Planning: Finding the best use of material, labor, machinery and other resources to maximize productivity and profitability.
The underlying problems typically involve many integer constraints, classifying them as NP-hard problems that require advanced computational techniques to solve efficiently.
Advancing Large-Scale LP Optimization: From PDLP to Simplex
The Primal-Dual Hybrid Gradient (PDLP) method, introduced by Google Research in 2021, is a groundbreaking first-order method (FOM) technique for solving large-scale linear programming (LP) problems. This technique iteratively optimizes the objective function while minimizing constraint violations using problem derivatives.
NVIDIA cuOpt implements GPU-accelerated PDLP, leveraging NVIDIA CUDA and NVIDIA Hopper GPUs to achieve up to a 5,000x speedup over traditional CPU-based solvers on problems well suited to PDLP. This approach delivers solutions with 4 to 6 digits of relative accuracy, making it an excellent starting point for further optimization with SimpleRose solver.
The Simplex Method, developed by George Dantzig in 1947, remains a widely used algorithm for solving LPs by systematically finding the optimal solution while adhering to linear equality and inequality constraints.
SimpleRose Rapidly Optimizing Solver Engine (Rose) enhances the Simplex Method with a proprietary, highly parallelized approach, enabling highly accurate solutions. Built for the massive parallelism of NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchips and NVIDIA GB200 Grace Blackwell-accelerated systems, Rose pushes the boundaries of scalability and computational efficiency.
With breakthrough parallel performance, Rose enables the solution of larger and more complex LP problems than ever before—unlocking new possibilities for decision optimization at an unprecedented scale.
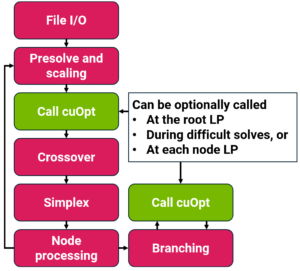
Accelerating MILP Optimization with the Rose+cuOpt Approach
Solving mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) problems involves breaking them down into a series of LP subproblems. The first step is typically solving a relaxed LP version, where integer constraints are ignored. This provides a lower bound (for minimization) or upper bound (for maximization) on the MILP solution. Faster Root LP solutions directly reduce total MILP solve time, making this step critical to optimization efficiency.
By leveraging cuOpt LP solver, Rose achieves up to 5.1x faster Root LP solutions, accelerating MILP problem-solving significantly.
The next step employs a mixture of techniques such as branch-and-bound and branch-and-cut where a tree of LPs is systematically solved to find feasible solutions for integer variables and prove optimality.
Optimizing MILP with Rose and cuOpt
After solving the Root LP, a combination of techniques—such as branch-and-bound and branch-and-cut—systematically explores a tree of LPs to find feasible integer solutions and prove optimality.
cuOpt further enhances MILP optimization by providing heuristic integer-feasible solutions, allowing Rose to prune unnecessary computations and solve MILPs up to 8.6x faster, while still ensuring high accuracy and provable optimality.
The Best of Both: Rose+cuOpt Integration
The integration of Rose and cuOpt brings together the strengths of both solvers:
- cuOpt quickly finds a near-optimal solution to the Root LP.
- A crossover algorithm seeds Rose’s Simplex method with cuOpt solution, aligning it to a vertex on the LP polytope.
- Rose refines the solution using proprietary Simplex method, ensuring the highest level of accuracy required for real-world optimization problems.
Not every LP problem is ideal for PDLP methods, so Rose utilizes cuOpt asynchronously in a fire-and-forget approach. This parallel execution ensures that cuOpt only serves as an accelerator, never increasing solve time—offering guaranteed performance gains for customers.
LP Performance: Speeding Up Optimization with Rose+cuOpt
The chart below illustrates the performance boost achieved by Rose using cuOpt across several LP benchmark problems.
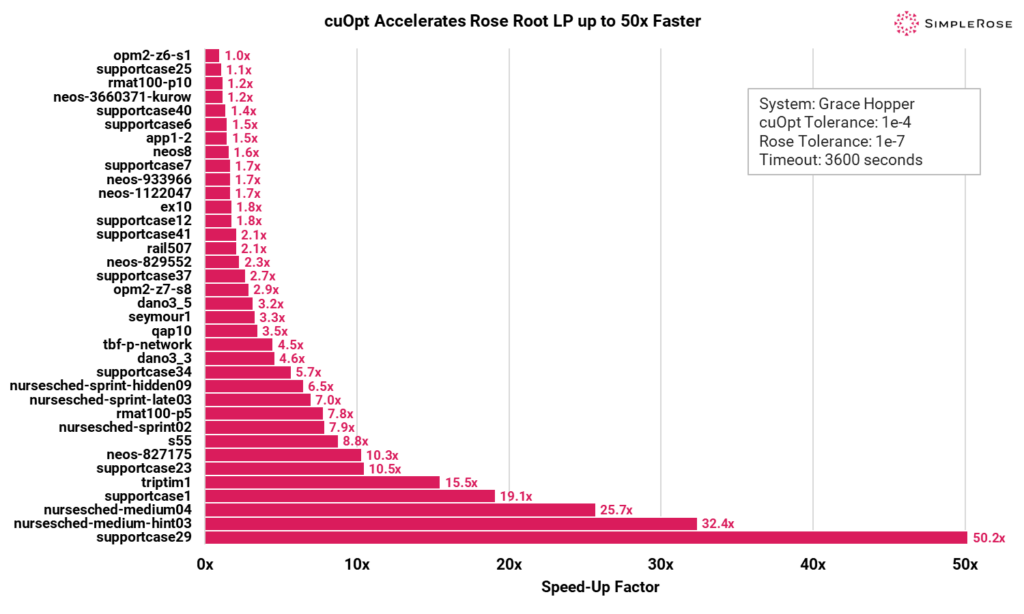 For root LP problems accelerated by Rose+cuOpt, we observed up to 50.2x speedup compared to using Rose alone. The most significant improvement was seen in scheduling problems, such as nursesched-medium-hint03.
For root LP problems accelerated by Rose+cuOpt, we observed up to 50.2x speedup compared to using Rose alone. The most significant improvement was seen in scheduling problems, such as nursesched-medium-hint03.
Why QAPs Benefit from cuOpt Acceleration
QAPs are a family of optimization problems that involve assigning facilities to locations while considering pairwise distances and flows as constraints. The significant speedup on QAPs is due to the favorable geometry of the hyperplanes within the underlying MILP formulation.
In general, shallower angles in the optimization space are easier for first-order methods like PDLP to process efficiently. Since this kind of geometry is typical in many MILPs, cuOpt acceleration approach proves highly effective across a wide range of optimization problems.
MILP Performance: How Rose+cuOpt Enhances Large-Scale Optimization
A key feature of cuOpt is its ability to generate heuristic solutions for MILP problems. By running its internal algorithm, cuOpt quickly produces a high-quality initial integer solution. While not guaranteed to be optimal, these solutions are feasible and often very close to the best possible.
Below are comparisons of how Rose, when combined with cuOpt heuristic, performs on MIPLIB benchmark problems. For MILP problems accelerated by Rose+cuOpt, we observed up to 61.7x speedup on overall solve time compared to using Rose alone.
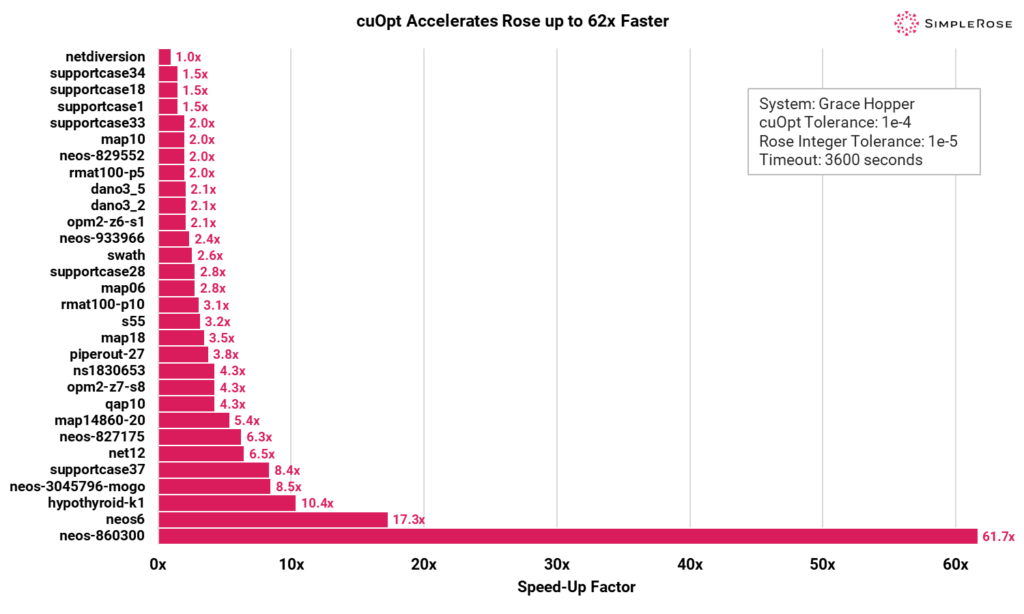 Accelerating MILP Solving with cuOpt Heuristics
Accelerating MILP Solving with cuOpt Heuristics
By leveraging cuOpt’s fast heuristic solutions, Rose significantly reduces MILP solve times. This is achieved through a parallel approach, where:
- cuOpt quickly computes a heuristic integer solution.
- Rose runs concurrently, using the heuristic solution returned to prune the MILP search tree.
- This pruning minimizes the search space, allowing Rose to converge faster.
As a result, this synergistic approach enables faster, more efficient MILP solving, making it ideal for large-scale optimization problems.
Unlock Faster, Smarter Optimization with SimpleRose
SimpleRose specializes in high-performance optimization solutions, turning complex business challenges into actionable strategies. Our cloud-based Rose solver offers a low-barrier entry, eliminating the need for software installation, configuration, and hardware maintenance.
With intuitive “fire-and-forget” ease of use, always-on activity logs, and detailed solve metrics, SimpleRose makes advanced optimization accessible to businesses of all sizes. Our expert support team ensures seamless adoption and integration, whether you’re new to optimization or looking to enhance operations.
Let SimpleRose help you optimize supply chains, work scheduling, and resource allocation faster and more efficiently.